In a world filled with vast amounts of information, effective learning strategies are essential. One powerful tool for enhancing memory retention is spaced repetition. Whether you’re a student preparing for exams, a professional looking to improve knowledge retention, or someone interested in lifelong learning, understanding and applying spaced repetition can significantly boost your ability to recall information over time. This article will delve into the concept of spaced repetition, its benefits, and how you can implement it for better retention in your learning routine.
Understanding Spaced Repetition
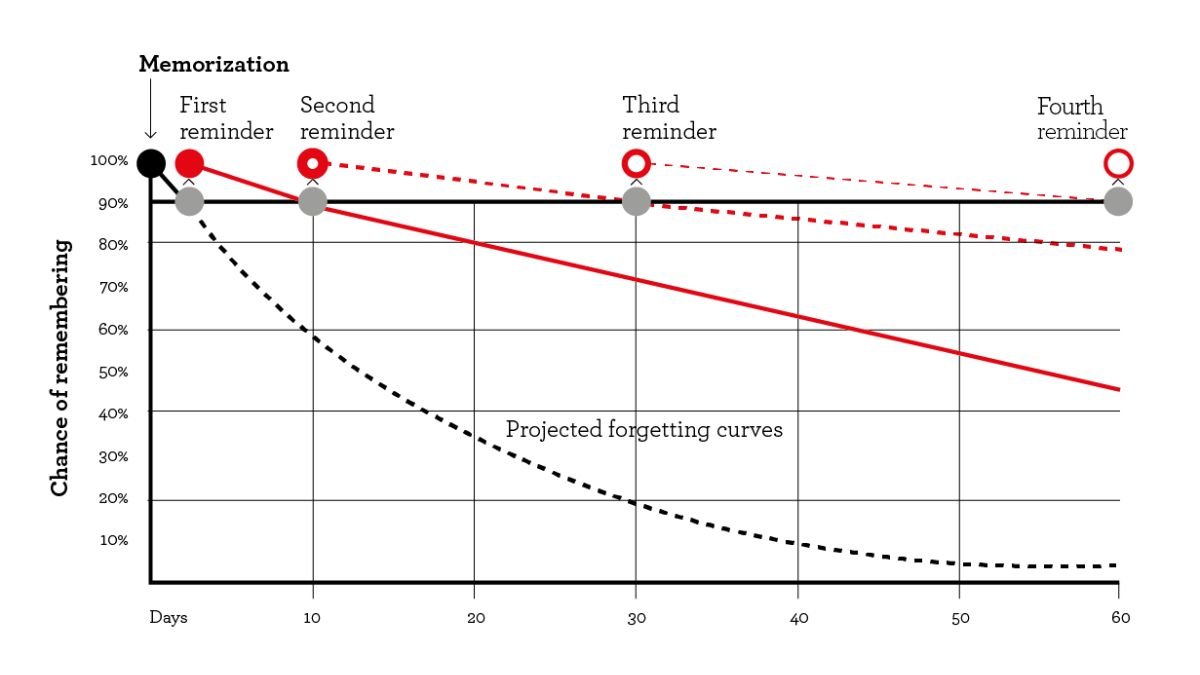
Spaced repetition is a learning technique that involves reviewing information at gradually increasing intervals. The core idea is to recall information just before you’re likely to forget it, thereby strengthening your memory of it. This method leverages the “forgetting curve,” a theory that shows how information is lost over time when there is no attempt to retain it. By spacing out review sessions, you combat the forgetting curve, ensuring that knowledge stays fresh in your mind for longer periods.
The science behind spaced repetition is rooted in cognitive psychology. When we first learn something new, it is stored in our short-term memory. However, unless this information is revisited, it often fades away, as our brains prioritize new or more critical inputs. Spaced repetition helps transfer knowledge from short-term to long-term memory by periodically refreshing it before it is forgotten.
This technique works because it aligns with how our brains naturally process and store information. By revisiting material at the right intervals, you force your brain to recall it actively, which solidifies it in your long-term memory. The intervals of repetition can be adjusted depending on how well you know the information. Initially, shorter intervals are needed, but as your retention improves, the intervals can be extended.
The Forgetting Curve and Spacing Intervals
The forgetting curve, introduced by Hermann Ebbinghaus in the 19th century, illustrates how rapidly we forget newly learned information without reinforcement. His research found that without consistent review, we forget about 50% of new information within an hour and nearly 70% within 24 hours. By day 7, retention plummets to around 20% without any active recall.
Spaced repetition counters this natural decline in memory. Here’s how it works:
- First Interval (After Initial Learning): After you’ve learned something new, review it within 24 hours to reinforce the memory.
- Second Interval (After a Few Days): Review the material again after 2-3 days to further solidify it.
- Third Interval (After a Week): Test your recall about a week later to strengthen the memory even more.
- Longer Intervals: Continue reviewing the information at increasingly longer intervals—every two weeks, then a month, and so on.
These intervals are not set in stone, and various apps and algorithms can help tailor them based on individual performance. The goal is to find the sweet spot where you’re challenging your memory just enough to recall the information without completely forgetting it.
The Benefits of Spaced Repetition
Spaced repetition offers numerous benefits for learners of all types. Here are some of the most significant advantages:
1. Improved Long-Term Retention
The most obvious benefit of spaced repetition is improved long-term retention. By spacing out your reviews, you ensure that information is consistently brought back to the forefront of your mind, making it easier to retain over extended periods. This is particularly useful for subjects that require a deep understanding and retention of complex material, such as language learning, medical studies, or preparing for major exams.
2. Efficient Learning
Spaced repetition maximizes learning efficiency by reducing the need for constant cramming or re-reading of material. Instead of repeatedly reviewing the same material in a single session, which can lead to diminishing returns, spaced repetition encourages brief but focused reviews at optimal intervals. This saves time and prevents burnout while ensuring that the information sticks.
3. Active Recall Enhancement
Spaced repetition involves active recall, a process in which learners retrieve information from memory rather than passively re-reading it. Active recall has been shown to be a highly effective learning strategy because it strengthens neural pathways related to the information being recalled. Each time you actively remember something, you reinforce its place in your long-term memory.
4. Customized Learning
Another benefit of spaced repetition is that it can be tailored to the individual learner. Some information may be easier to remember, while other content may require more frequent reviews. Modern spaced repetition systems (SRS) use algorithms that track your performance and adjust the intervals for each piece of information based on how well you recall it.
5. Reduces Cognitive Load
Cognitive overload can be a major obstacle to learning. By spacing out learning sessions and focusing on manageable chunks of information, spaced repetition reduces the cognitive load. This allows learners to process and absorb information without feeling overwhelmed, which improves overall understanding and retention.
Implementing Spaced Repetition in Your Learning Routine
Using spaced repetition effectively requires planning and consistency. Here are some practical steps to integrate this technique into your learning routine:
1. Choose the Right Tools
There are several tools available to help you implement spaced repetition. Popular apps like Anki and Quizlet offer spaced repetition features that adjust review intervals based on how well you remember each card. Anki, for example, uses an algorithm that adapts to your individual learning pace, ensuring that you review information just before you’re likely to forget it.
For those who prefer a more hands-on approach, you can create your own system using flashcards. Write questions or prompts on one side and answers on the other. As you review each card, sort them into different piles based on how well you remember the information. Review the more challenging cards more frequently, and the easier ones less often.
2. Break Material into Smaller Chunks
Instead of trying to learn everything in one go, break the material into smaller, manageable chunks. Spaced repetition works best when you’re not overwhelmed by the amount of information you’re trying to retain at once. This also allows you to focus on mastering one concept before moving on to the next, making your study sessions more effective.
3. Consistency is Key
Consistency is crucial when using spaced repetition. Make sure to schedule regular study sessions and stick to them. Missing a review session can cause you to forget important information, forcing you to go back and relearn it. Set aside specific times during the day for your reviews, and gradually increase the intervals between sessions as you become more comfortable with the material.
4. Use Multiple Forms of Review
While spaced repetition primarily focuses on reviewing information at intervals, it can be even more effective when combined with other learning methods. Try using different forms of review, such as reading, writing, and speaking the information aloud. These varied approaches engage different parts of the brain, helping to reinforce your learning.
5. Monitor Your Progress
As you continue to use spaced repetition, track your progress to see how well you’re retaining information. Many spaced repetition apps provide insights into your performance, showing you which areas you’re excelling in and where you need more practice. Use this data to adjust your study plan, focusing more on the areas where you’re struggling and increasing the intervals for topics you’ve mastered.
Applications of Spaced Repetition in Various Fields
1. Language Learning
Spaced repetition is highly effective in language learning. Whether you’re trying to master vocabulary, grammar rules, or pronunciation, reviewing language concepts at spaced intervals helps reinforce them in your memory. Apps like Anki are commonly used by language learners to memorize thousands of words and phrases.
2. Medical and Professional Exams
In fields that require the retention of a large amount of information, such as medicine, law, or engineering, spaced repetition is invaluable. Medical students, for example, often use this technique to memorize complex facts, terminology, and procedures, ensuring that the information is readily accessible when needed.
3. Professional Development
Spaced repetition can also be used in professional development. For instance, if you’re learning new software, business strategies, or industry regulations, using spaced repetition will help you internalize these concepts for long-term career advancement.
Conclusion
Spaced repetition is a proven technique for improving retention and ensuring that knowledge stays fresh in your memory. By leveraging the power of active recall and reviewing material at optimal intervals, learners can significantly enhance their long-term retention. Whether you’re preparing for exams, learning a new language, or acquiring new skills for your profession, spaced repetition can be a valuable tool in your learning arsenal. With the right tools, consistency, and strategies, anyone can use spaced repetition to become a more effective learner.