In an age where digital privacy is increasingly threatened, protecting our online information has become a top priority. Whether you are browsing the web casually, conducting business transactions, or streaming media, ensuring the safety of your data is crucial. One of the most effective tools for enhancing online privacy and security is a Virtual Private Network (VPN). When combined with broader cybersecurity measures, VPNs form a robust defense system to safeguard our online presence. This article explores the intricate relationship between VPNs and cybersecurity, and how they work together to protect users from digital threats.
Understanding VPNs: A Key Tool for Online Privacy
What is a VPN?
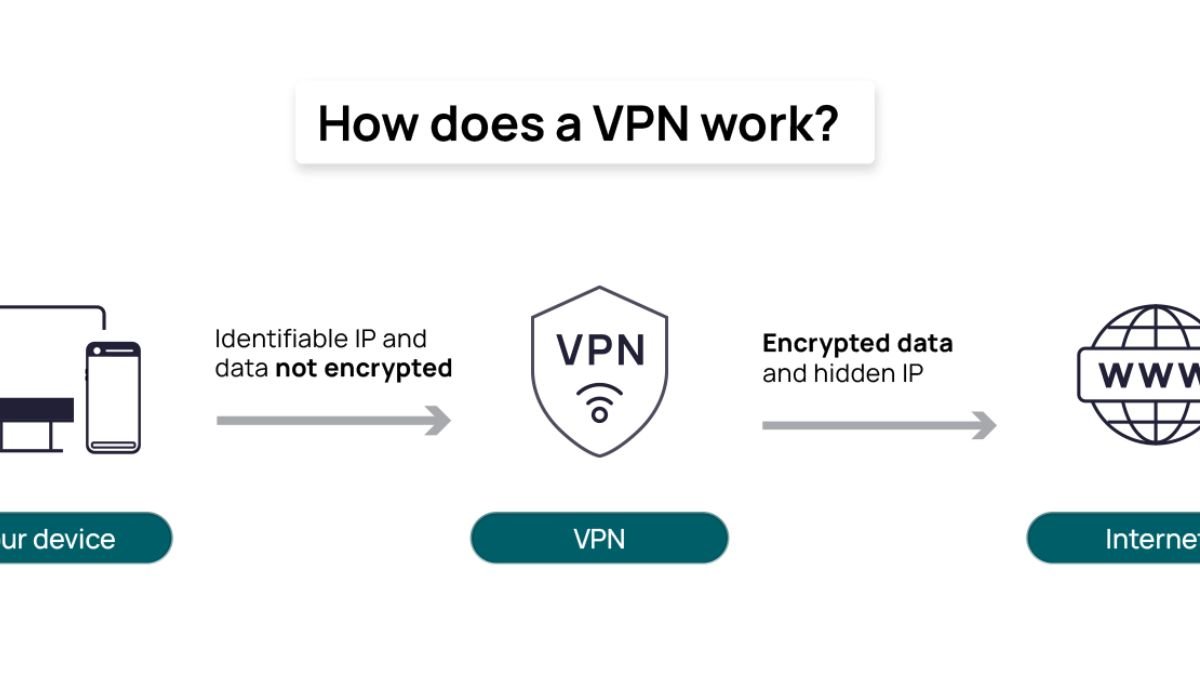
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technology that allows users to create a secure and encrypted connection over a less secure network, typically the internet. VPNs act as a tunnel for your data, encrypting it as it passes between your device and the destination server. This means that even if hackers or malicious actors intercept the data, they cannot decipher it without the encryption key.
A VPN achieves its privacy by masking the user’s IP address, which is a unique identifier for your internet connection. Instead of using your own IP address, the VPN assigns a temporary one from a different location, making it harder for websites, advertisers, or hackers to trace your activities back to you. This capability is especially useful for protecting your identity when accessing public Wi-Fi networks, which are often hotspots for cyberattacks.
Types of VPNs
There are different types of VPNs, each serving a specific purpose based on the level of security needed or the user’s intent:
- Remote Access VPN: These VPNs allow individuals to connect to a private network remotely. This type is commonly used by remote workers to securely access company resources from any location.
- Site-to-Site VPN: Often used by businesses, a site-to-site VPN connects multiple networks over the internet. For example, a company might connect its offices located in different geographical regions securely.
- Personal VPN: This is the type of VPN most consumers use to protect their privacy online. It is commonly used for activities like anonymous browsing, secure downloads, and accessing geo-restricted content.
Each type of VPN provides a layer of privacy and security, which is a crucial element in the broader scope of cybersecurity.
The Role of Cybersecurity in Protecting Data
What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity refers to the practices, technologies, and processes designed to protect computers, networks, and data from cyberattacks, unauthorized access, and damage. With the increase in sophisticated cyber threats, the need for strong cybersecurity measures has never been more essential.
Cybersecurity encompasses various elements, including:
- Network Security: Protecting the integrity and usability of a network.
- Information Security: Safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Operational Security: Managing how data is handled and processed.
- Disaster Recovery: Ensuring systems can be restored in the event of a security breach or data loss.
Without effective cybersecurity, personal, business, and governmental data is at risk of being exploited by cybercriminals.
Common Cybersecurity Threats
To understand how VPNs and cybersecurity work together, it is important to grasp the nature of the threats they combat. Some common cybersecurity threats include:
- Malware: Malicious software designed to damage or exploit systems, such as viruses, worms, and ransomware.
- Phishing: A social engineering attack where attackers trick individuals into providing sensitive information, such as login credentials.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Cybercriminals intercept data transmitted between two parties to steal information or alter communication.
- DDoS Attacks: Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks overwhelm a network or website with traffic, causing it to crash and become unavailable.
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to confidential data, often resulting in identity theft, financial loss, or other personal damages.
While VPNs alone cannot protect against all these threats, they form a critical part of a layered cybersecurity strategy.
How VPNs Enhance Cybersecurity
Encryption and Data Protection
The primary way VPNs contribute to cybersecurity is through encryption. When you connect to the internet via a VPN, all data transmitted from your device is encrypted, making it unreadable to anyone trying to intercept it. This is especially important when using public or unsecured networks, where hackers often lurk, waiting to steal sensitive information such as passwords or credit card numbers.
The encrypted tunnel created by a VPN ensures that even if an attacker manages to access the data, it remains indecipherable without the proper decryption keys. This level of encryption is vital for activities like online banking, conducting business transactions, or sending confidential emails.
Masking Your IP Address
Another way VPNs enhance cybersecurity is by masking your real IP address. Your IP address can reveal a lot of information about you, such as your geographical location, your internet service provider, and your browsing history. By using a VPN, your real IP address is hidden and replaced with the VPN’s IP address, making it harder for third parties, such as advertisers or hackers, to track your online activities.
This anonymity protects you from targeted cyberattacks and helps prevent identity theft, as it becomes much more challenging for hackers to link your online behavior to your actual identity.
Preventing Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
A common tactic used by cybercriminals is a man-in-the-middle (MitM) attack, where they intercept communications between two parties. For example, if you are using an unsecured Wi-Fi network at a coffee shop, a hacker could intercept the data you are sending, including passwords or personal information.
A VPN mitigates this risk by encrypting the data being transmitted between your device and the destination server, making it nearly impossible for attackers to decipher the information they intercept. This encryption ensures that even if a hacker performs a MitM attack, the stolen data will be useless.
Protecting Against Phishing and Malware
While VPNs primarily protect against data interception and unauthorized access, many VPN services also include additional cybersecurity features. Some VPN providers offer integrated anti-malware and anti-phishing tools. These tools help detect and block malicious websites or emails before they can infect your device or trick you into sharing sensitive information.
While these additional features are not a replacement for dedicated antivirus software or other cybersecurity measures, they add an extra layer of protection when navigating the internet.
Limitations of VPNs in Cybersecurity
VPNs are Not a Standalone Solution
Despite their significant benefits, it is important to recognize that VPNs are not a cure-all for cybersecurity. They are a critical part of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy but should be used in conjunction with other measures, such as firewalls, antivirus software, and regular software updates.
For instance, while a VPN can encrypt your data and mask your IP address, it cannot protect you from all types of cyber threats. For example, if you download a malicious file or visit a compromised website, a VPN will not prevent malware from infecting your device. Similarly, a VPN will not protect against phishing attacks if you voluntarily provide sensitive information to a fraudulent website.
Data Logging by VPN Providers
Another concern is that not all VPN providers offer the same level of privacy. Some VPN services may log your data or share it with third parties. It is essential to choose a reputable VPN provider with a strict no-logs policy to ensure your online activities remain private.
The Synergy of VPNs and Cybersecurity Measures
Layered Security Approach
The most effective way to ensure robust online protection is by combining VPNs with other cybersecurity tools and best practices. This approach, known as layered security, provides multiple lines of defense against cyber threats. For example, using a VPN alongside strong passwords, two-factor authentication, and antivirus software creates a more comprehensive security solution.
A VPN protects your data in transit, but strong cybersecurity habits, such as avoiding suspicious links and regularly updating software, help prevent malware infections and data breaches. By using VPNs and other cybersecurity measures together, you can greatly reduce the risk of falling victim to cyberattacks.
Education and Awareness
An essential component of cybersecurity is awareness. Understanding how VPNs work and how they fit into a broader cybersecurity framework is key to protecting yourself online. Regularly educating yourself about new cyber threats and staying updated on best practices can further enhance your online security.
Conclusion
VPNs play a crucial role in enhancing cybersecurity by encrypting data, masking IP addresses, and protecting users from common cyber threats like man-in-the-middle attacks. However, VPNs should not be viewed as a standalone solution. They are most effective when combined with other cybersecurity measures, such as firewalls, antivirus software, and good security habits. By working together, VPNs and cybersecurity measures can create a powerful defense system to protect against the ever-evolving landscape of digital threats.